Perfectly add Google Analytics to a site to measure website data and gather visitor insights, using Google Tag Manager and verify that it is working properly.
🚀 Goal: To add Google Tag Manager to a WordPress site.
🤞 Ideal Outcome: Google Tag Manager is properly installed without any technical issues.
🤔 Why this is important: Google Tag Manager is a great tool to add and manage multiple pixels and tracking codes without needing to edit the code of a site.
🧐 Where this is done In your WordPress install and Google Tag Manager.
🗓️ When this is done: Only once, the first time you install Google Tag Manager.
👨 Who does this: The person responsible for website management or analytics.
⚠️Prerequisites or requirements: This exact process only applies to WordPress.org sites.
Environment setup
Important: This SOP works only for self-hosted WordPress sites, aka WordPress.org and not WordPress.com
01▸ Download the Google Tag Assistant Companion (Free).
02▸ To sign up for Google Tag Manager (Free), you’ll need to log in to your Google account.
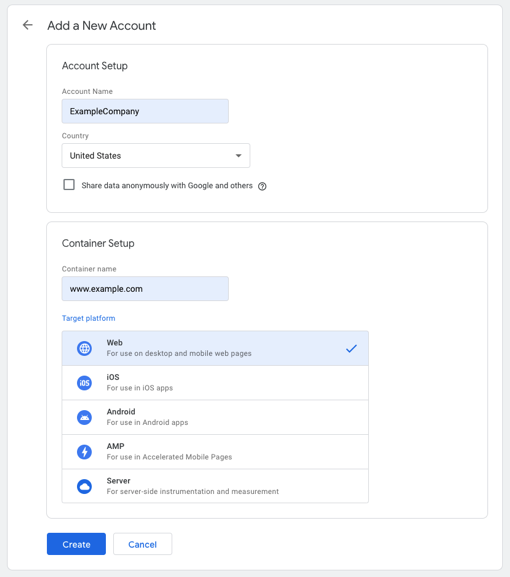
03▸ If this is your first time creating a Google Tag Manager Account, you’ll be redirected to the account creation page.
04▸ Fill in the following information:
- Account Name — The name you use to identify this account.
- Country — Country origin.
- Container name — Insert the URL of your website
- Target platform — Where do you plan to add Google Tag Manager (e.g. on your website, mobile, etc)
- (Optional) Share data anonymously with Google.
05▸ Once finished. Click “Create”.
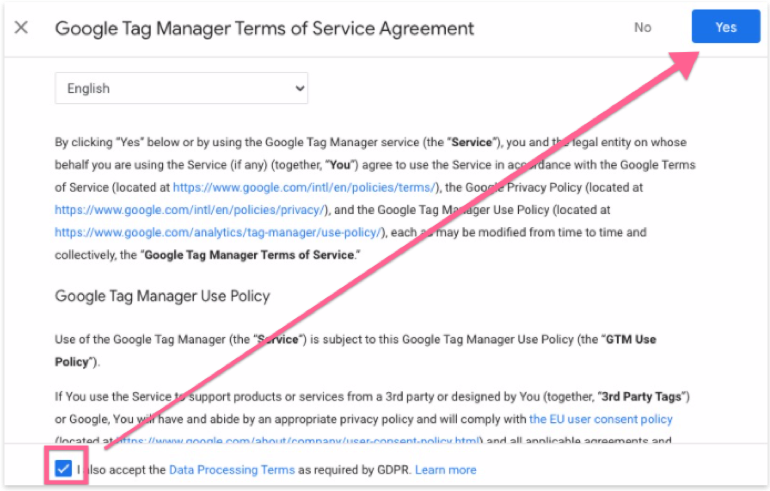
06▸ You’ll see a Google Tag Manager Terms of Service pop-up. Select the checkbox and click “Yes”.
07▸ You will see the code for installing Google Tag Manager. Ignore this since you won’t be manually adding code to your WordPress site. Click “OK”.
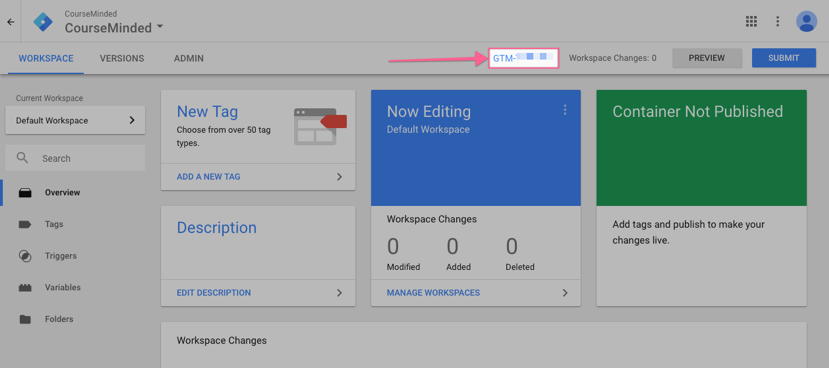
Once you are in your Workspace, make a note of your Google Tag Manager ID.
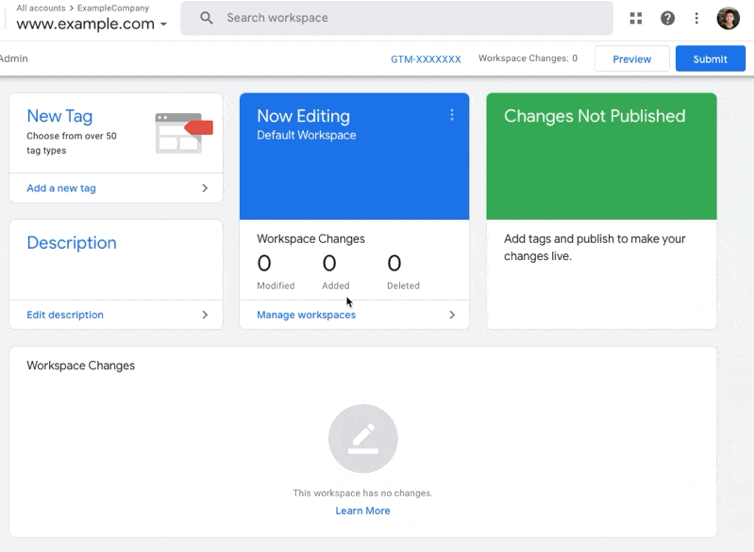
08▸ Click on “Submit” > “Publish” > Continue to publish your Google Tag Manager container and that’s it!
Install and configure the Google Tag Manager WordPress plugin
01▸ Log into your WordPress site.
02▸ In the WordPress sidebar, go to “Plugins” > “Add New”.
03▸ Enter “Google Tag Manager for WordPress” in the search box.
04▸ Install the GTM4WP plugin (the image may vary).
05▸ To activate the plugin, go to the WordPress sidebar and click “Settings” > “Google Tag Manager”.
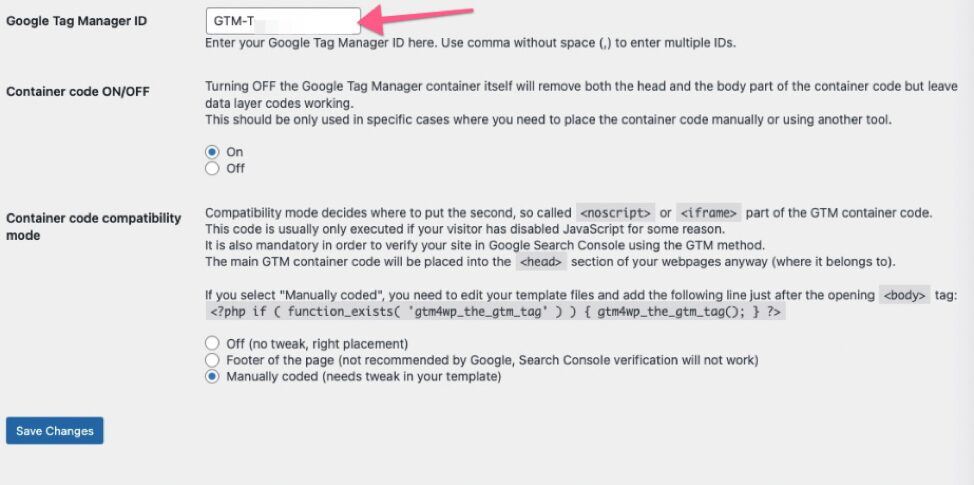
06▸ Paste your Google Tag Manager ID (the one you got from the Google Tag Manager dashboard) in the available field.
07▸ The plugin offers several ways to install the container code on your site. Before you implement any of these, we recommend you create a backup of your site.
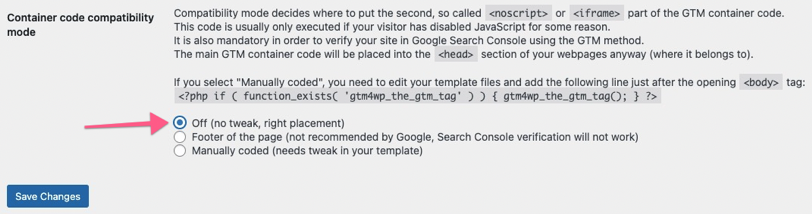
- Option 1: Off — with this option, the plugin will try to figure out the right placement for the container for you. This is the easiest option but there’s a small risk it might break something on the front end of your site. If you decide to go with codeless injection, select this option from the list and click “Save changes”
After selecting this, visit the website in a new tab or window and make sure everything looks right. If it does, you can move on to the next step of QA-ing the installation
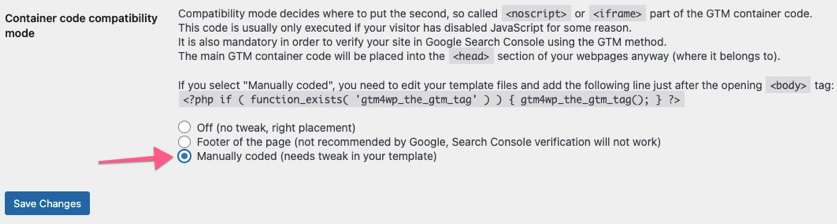
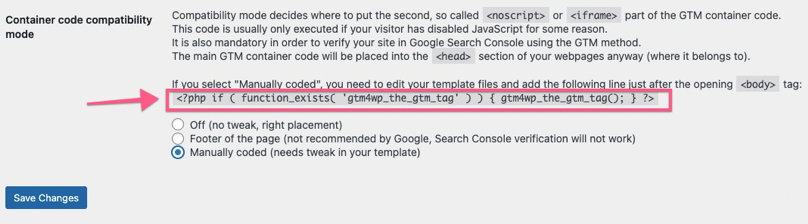
- Option 2: Manually Coded — with this option, you will need to make a small edit to your theme files. If your WordPress theme allows you to make changes and you’re comfortable with the theme editor, you can use this option. Select the “Custom (needs a tweak in your template)” container code placement and click on “Save Changes.”
08▸ Copy the PHP code provided by the plugin and click on “Save Changes”.
09▸ In the WordPress sidebar, go to “Appearance” > “Theme Editor”.
10▸ Make sure that you are editing the theme that you currently have installed on your site (you can go to “Appearance” > “Themes” to check the name of the theme you are using).
11▸ Select the “Theme Header” template from the list on the right.
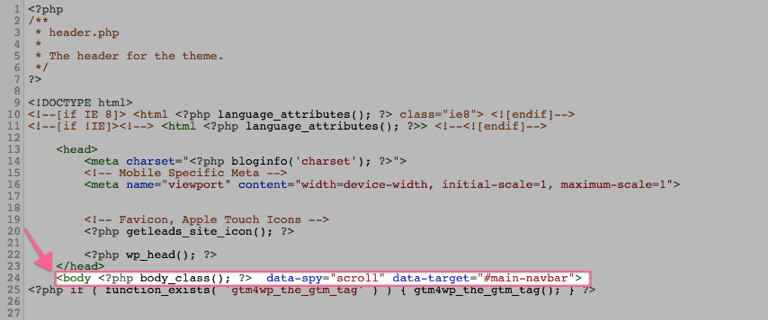
12▸ This template is different depending on the theme that you have installed. However, you will always be able to find an opening <body> tag in the code.
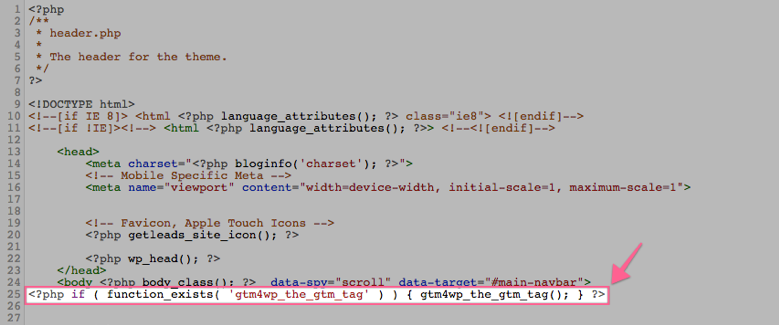
13▸ Paste the PHP code provided by the plugin right below the opening <body> tag.
14▸ Click on “Update File”.
QA your installation
Step 1: Confirm GTM Snippet Installation
Before testing with Tag Assistant, confirm that the GTM container code is correctly embedded in your website.
01▸ Open your website homepage using Chrome.
02▸ Right-click on the page and select “View Page Source”.
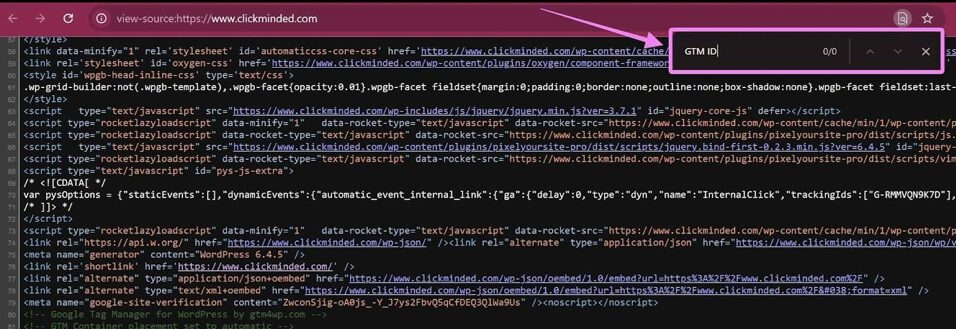
03▸ Press Ctrl + F (or Command + F on Mac) and search for your GTM ID (e.g., GTM-XXXXXX).
04▸ If you do not see the GTM ID in the source code:
- The container is not properly installed.
- Double-check that you’ve added the GTM snippet correctly in your site’s header and body sections as outlined in SOP 004.
- If using a CMS like WordPress, verify that your GTM plugin or theme settings include the correct ID.
Step 2: Use GTM’s Native Preview Mode (Recommended)
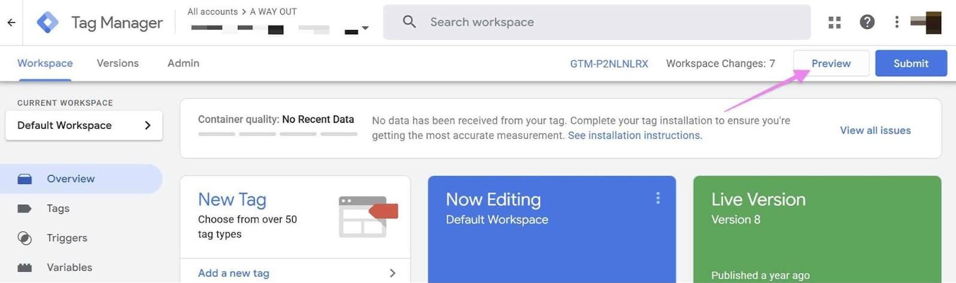
05▸ Go to Google Tag Manager and open your container.
06▸ Click the “Preview” button in the top right.
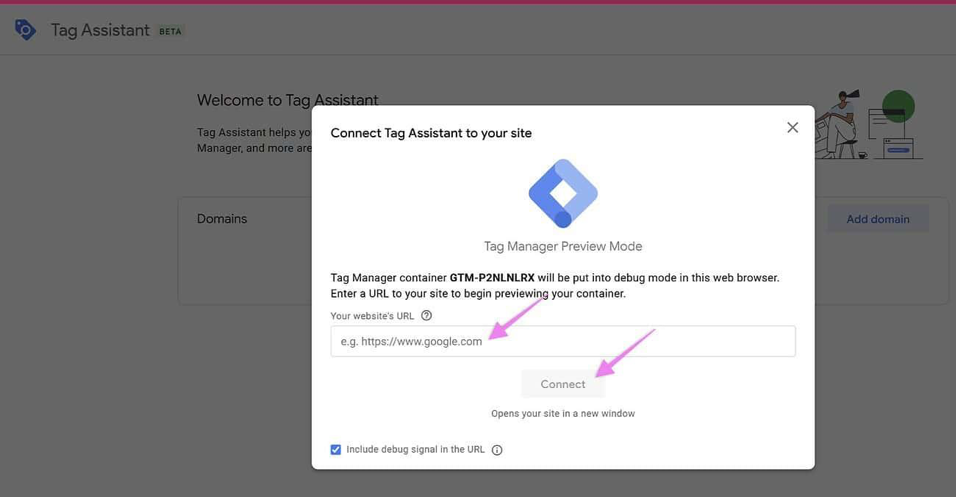
07▸ Enter your website URL in the pop-up window and click “Connect”.
08▸ A new window will open showing your site with a debug console at the bottom.
If the GTM installation is correct, you’ll see tags being fired in the debug console.
Step 3: (Optional) Use Google Tag Assistant Companion Extension
If you prefer or need to use the Chrome extension:
09▸ Install and open the Google Tag Assistant Companion icon on your browser.
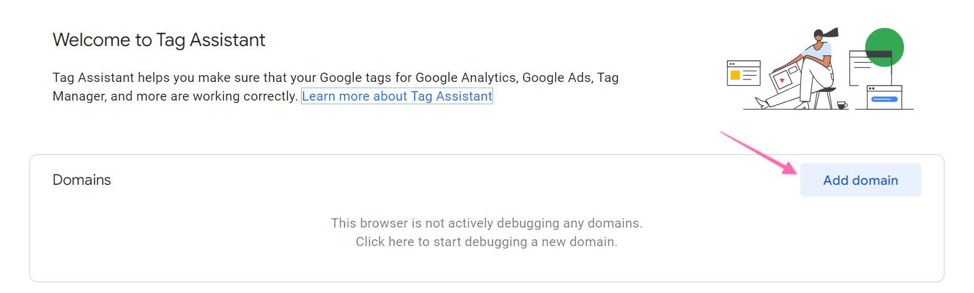
10▸ Click on “Add domain”.
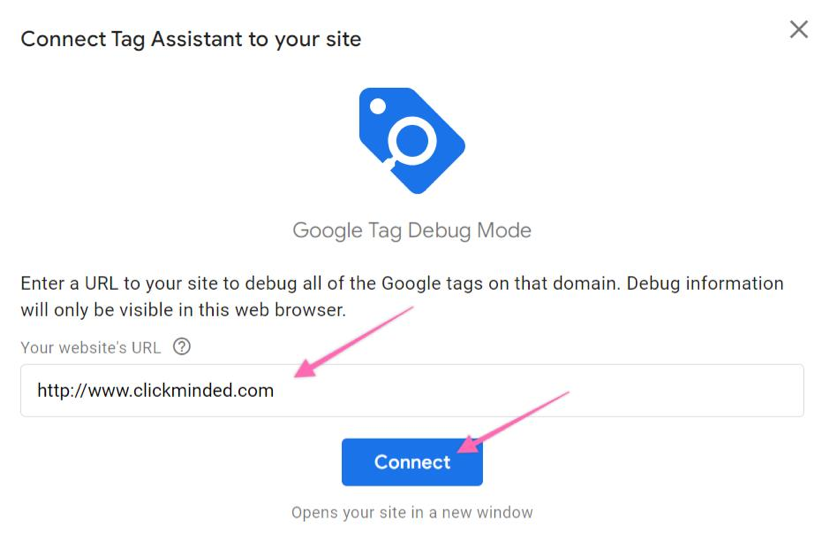
11▸ Enter your website URL, click “Connect” and reload the page.
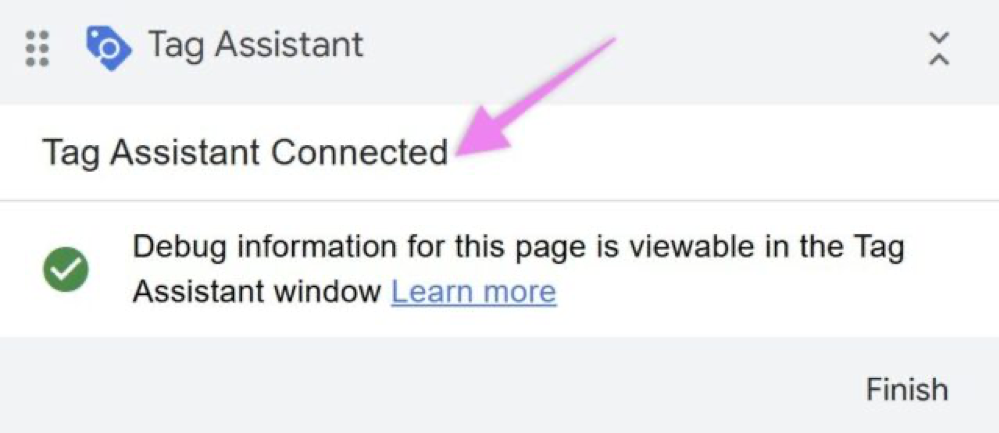
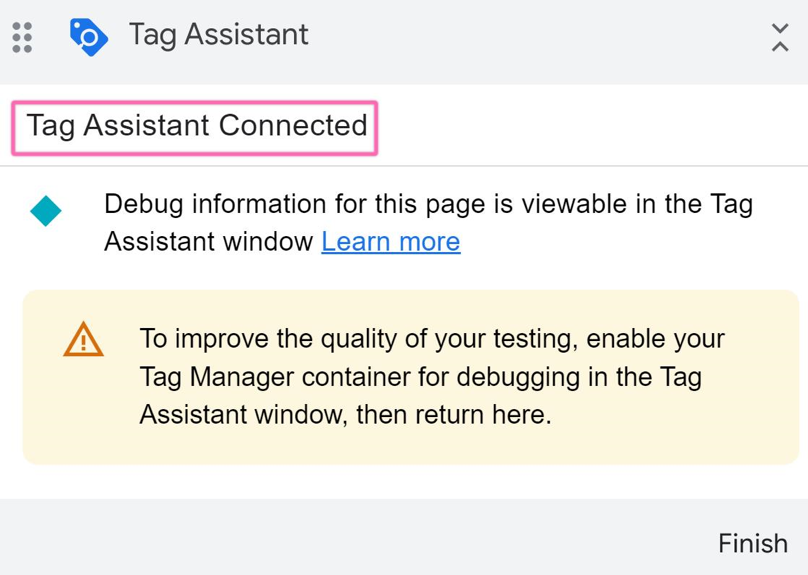
12▸ If successful, a message saying Tag Assistant Connected will appear.
Note: If this fails, but Step 2 works, rely on GTM’s built-in preview mode for debugging instead. If connection issues occur, you may refer to this link here to troubleshoot.
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Still not seeing your GTM ID in your site’s source code? Revisit SOP 004 and ensure the container is added to the correct parts of your site.
- Make sure your website isn’t cached (clear your browser cache or try an incognito window).
- If using a CMS, confirm that third-party plugins or themes are not stripping scripts.